AGV for Warehouse Automation: The Future of Smart Logistics
As global supply chains accelerate and customer expectations rise, warehouse automation has become essential for achieving efficiency, accuracy, and speed. Among all automation technologies, AGVs (Automated Guided Vehicles) play a critical role by streamlining material movement, reducing labor dependency, and enabling 24/7 intelligent logistics operations. This article explores how AGVs transform warehouse workflows and why they are a key component of modern automated facilities.

What Are AGVs in Warehouse Automation?
AGVs for warehouse automation are driverless vehicles designed to transport goods, pallets, and containers within a warehouse environment. They follow predefined routes using technologies like magnetic tape, laser guidance, vision-based navigation, or SLAM.
By replacing manual forklifts and pallet jacks, AGVs ensure safer, more consistent, and more efficient intralogistics operations.
How AGVs Work in Warehouses
AGVs operate using sensors, onboard computers, and wireless communication systems. They interact with a central fleet management platform that assigns tasks, avoids traffic congestion, optimizes paths, and monitors real-time operational status.
AGVs can automatically:
- Pick up and drop off pallets
- Move inventory between storage zones
- Support order picking operations
- Connect inbound and outbound logistics
Types of AGVs Used in Warehouses
Different AGV models support different warehouse tasks:
1. AGV Pallet Movers
Ideal for transporting pallets between receiving, storage, and shipping zones.
2. AGV Forklifts
Automate stacking, high-bay storage, and pallet handling operations.
3. Tugger AGVs
Pull multiple carts for batch material movement and restocking.
4. Unit Load AGVs
Transport boxes, totes, and containers with conveyors or lift decks.
5. Customized Warehouse AGVs
Designed for unique layouts, narrow aisles, or specialized material handling.
Key Benefits of Using AGVs in Warehouse Automation
1. Higher Efficiency and Productivity
AGVs operate continuously without breaks, improving workflow speed and eliminating delays caused by manual handling.
2. Improved Safety
With 360° sensors, automatic braking, and obstacle detection, AGVs significantly reduce workplace accidents.
3. Lower Operational Costs
Automating repetitive tasks helps reduce labor costs, training expenses, and errors.
4. Accurate and Consistent Movement
AGVs follow programmed paths precisely, ensuring consistent delivery and preventing inventory damage.
5. Scalable and Easy to Integrate
Warehouse operators can gradually expand the AGV fleet as business demand grows.
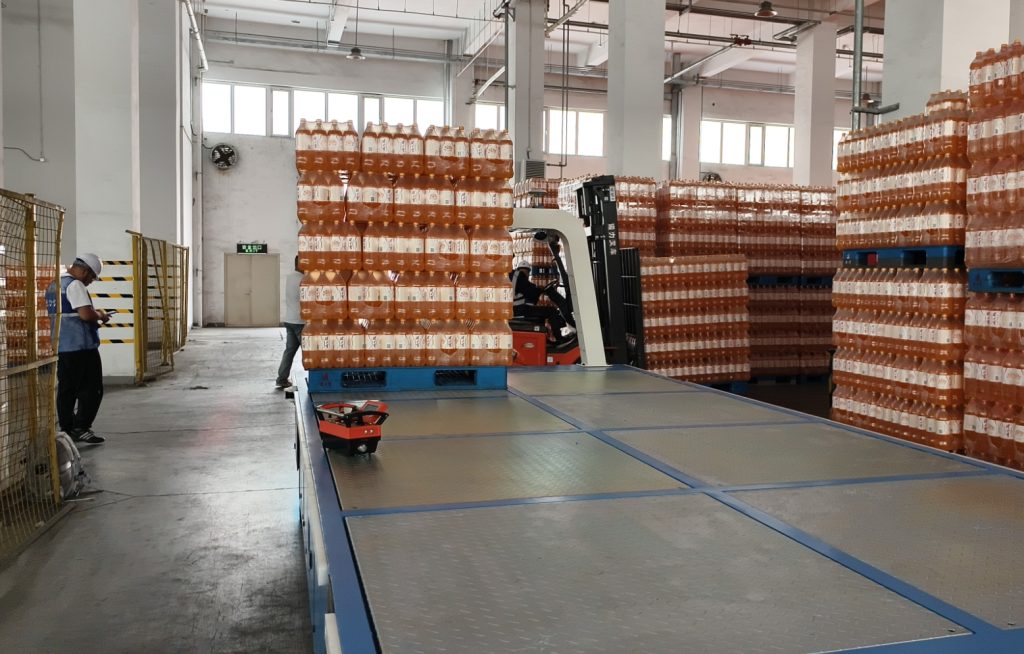
Applications of AGVs in Modern Warehouses
AGVs are widely used in e-commerce, retail, manufacturing, and third-party logistics (3PL). Key applications include:
- Pallet transport and staging
- Order picking assistance
- Production-to-warehouse transfer
- Automated loading and unloading support
- Cross-docking operations
AGVs vs. AMRs in Warehouse Automation
AGVs use fixed paths, making them ideal for predictable, structured environments.
AMRs (Autonomous Mobile Robots) use dynamic path planning and adapt to changing conditions.
Warehouses with stable workflows often prefer AGVs due to their safety, reliability, and cost-efficiency.
Why AGVs Are Essential for the Smart Warehouse Era
With Industry 4.0 and digital transformation, AGVs integrate seamlessly with WMS, ERP, and MES systems. This creates a fully connected warehouse environment where data drives efficiency and every material movement is tracked in real time.
AGVs enable smart, flexible, and highly efficient warehouse ecosystems ready for future growth.
Conclusion
AGVs for warehouse automation are transforming the logistics landscape by improving efficiency, safety, and cost-effectiveness. Whether handling pallets, supporting order fulfillment, or connecting different warehouse zones, AGVs offer a scalable and reliable automation solution. As warehouses continue to evolve toward intelligent operations, AGVs will remain a crucial element of modern intralogistics.