AGV Automated Guided Vehicle: The Ultimate Guide to Smart Material Handling



Introduction to AGV Automated Guided Vehicles
An AGV (Automated Guided Vehicle) is a driverless, computer-controlled machine designed to transport materials efficiently within industrial environments. As factories, warehouses, and logistics centers move toward automation, AGVs have become a core technology in modern material handling. Their precision, reliability, and scalability make them essential tools for businesses seeking to improve workflow efficiency and reduce operating costs.
What Is an AGV and How Does It Work?
An AGV Automated Guided Vehicle uses advanced navigation systems and onboard sensors to transport goods along predefined routes. These routes may be guided by magnetic tape, laser reflectors, QR codes, or natural feature navigation (SLAM).
AGVs are connected to a central control system that assigns tasks, manages traffic, and ensures safe, efficient movement across the facility. Through real-time communication, AGVs can avoid obstacles, monitor their surroundings, and complete transportation tasks accurately.
Core Navigation Technologies Used in AGVs
Modern AGVs rely on several navigation methods depending on the application and environment:
Magnetic Tape Guidance
Uses magnetic strips on the floor; cost-effective and easy to install.
Laser Guidance
Employs laser scanners and reflectors for high precision in complex layouts.
Vision or QR Code Guidance
Uses onboard cameras and recognition markers to navigate established routes.
SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping)
The most intelligent navigation method, where AGVs map their environment and update their routes in real-time without requiring physical markers.
Main Types of AGV Automated Guided Vehicles
AGVs come in various designs to support different workflows:
- AGV Forklifts: Automate pallet lifting, stacking, and storage tasks.
- Tugger AGVs: Pull multiple carts for assembly line supply.
- Unit Load AGVs: Carry boxes, trays, or components using conveyors or lift platforms.
- Pallet AGVs / Pallet Jacks: Ideal for pallet movement in warehouse operations.
- Custom AGVs: Tailored designs for industries requiring specialized functions.
Benefits of Using AGV Automated Guided Vehicles
AGVs deliver significant advantages that support industrial automation:
1. Increased Efficiency
AGVs operate continuously without fatigue, boosting productivity and reducing cycle times.
2. Enhanced Safety
Equipped with sensors and obstacle detection systems, AGVs minimize workplace accidents and product damage.
3. Labor Cost Reduction
Automation decreases manual handling requirements, allowing staff to focus on high-skill tasks.
4. High Accuracy and Consistency
AGVs follow precise routes, ensuring stable and error-free material handling.
5. Scalable and Flexible
Businesses can easily expand AGV fleets as operational demands grow.
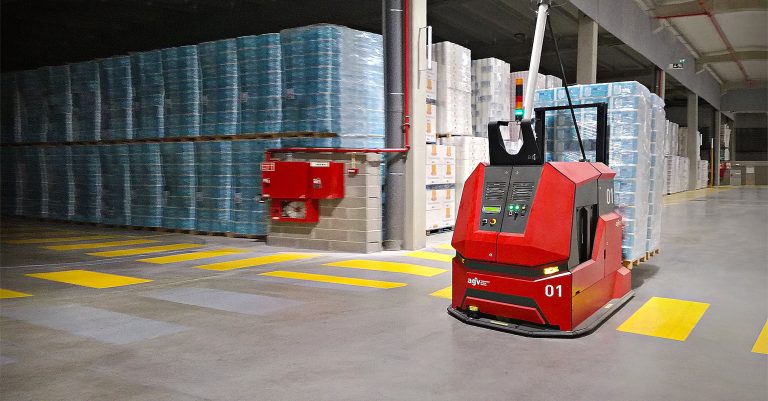
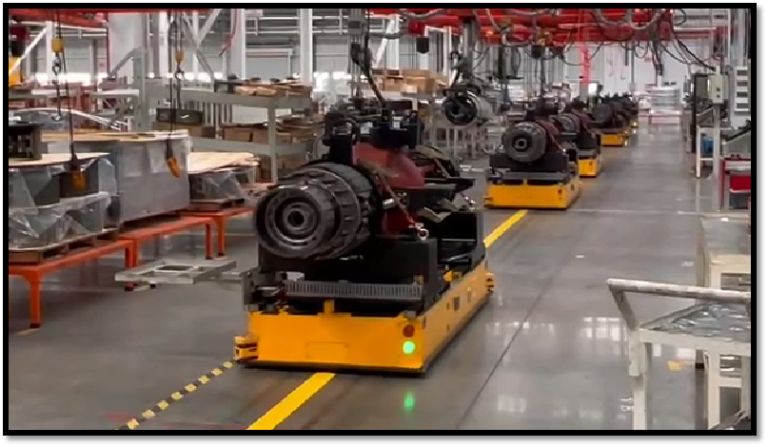
Industries That Use AGV Automated Guided Vehicles
AGVs are widely adopted across numerous industries:
- Manufacturing: Feeding assembly lines, transporting components, and managing WIP.
- Warehousing and Logistics: Pallet handling, inbound/outbound movement, order fulfillment.
- Automotive: Transporting engines, chassis, and heavy components.
- Food & Beverage: Hygienic and contamination-free material flow.
- Pharmaceuticals: Precise movement in cleanroom and controlled environments.
AGVs vs. AMRs: Key Differences
While AGVs follow fixed routes, AMRs (Autonomous Mobile Robots) navigate freely using AI-powered sensors and dynamic path planning.
AGVs are ideal for structured, predictable environments, while AMRs suit operations requiring high flexibility.
The choice depends on plant layout, automation goals, and budget.
Why AGVs Are Essential for Industry 4.0
AGVs play a crucial role in digital and smart manufacturing. When connected to ERP, WMS, and MES systems, they help achieve:
- Real-time material tracking
- Automated production flow
- Predictive scheduling
- Intelligent logistics management
AGVs act as the foundation for building a fully automated, data-driven factory.
Conclusion
AGV Automated Guided Vehicles are reshaping intralogistics by improving efficiency, safety, and operational consistency. Whether used in warehouses, production lines, or distribution centers, AGVs provide a scalable and reliable automation solution. As industries continue to adopt smarter material-handling technologies, AGVs will remain a key component of future-ready, intelligent factories.