Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs): The Complete Guide to Modern Material Handling
What Is an Automated Guided Vehicle (AGV)?
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) are driverless, computer-controlled machines designed to transport materials within industrial facilities. They move goods along predefined routes using navigation systems such as magnetic guidance, laser guidance, or SLAM. By automating internal logistics tasks, AGVs help companies reduce labor intensity, improve workflow efficiency, and eliminate human error in repetitive material-handling operations.



How Do AGVs Work?
AGVs operate through a combination of sensors, navigation technologies, and centralized control systems.
They may use magnetic tape installed on the floor, laser reflectors placed around the facility, or advanced SLAM navigation that scans natural landmarks to build maps. Wireless communication connects AGVs to a fleet management system that assigns tasks, monitors traffic, and ensures safe operation. With real-time data exchange, AGVs maintain accurate movement, avoid obstacles, and deliver materials precisely where needed.
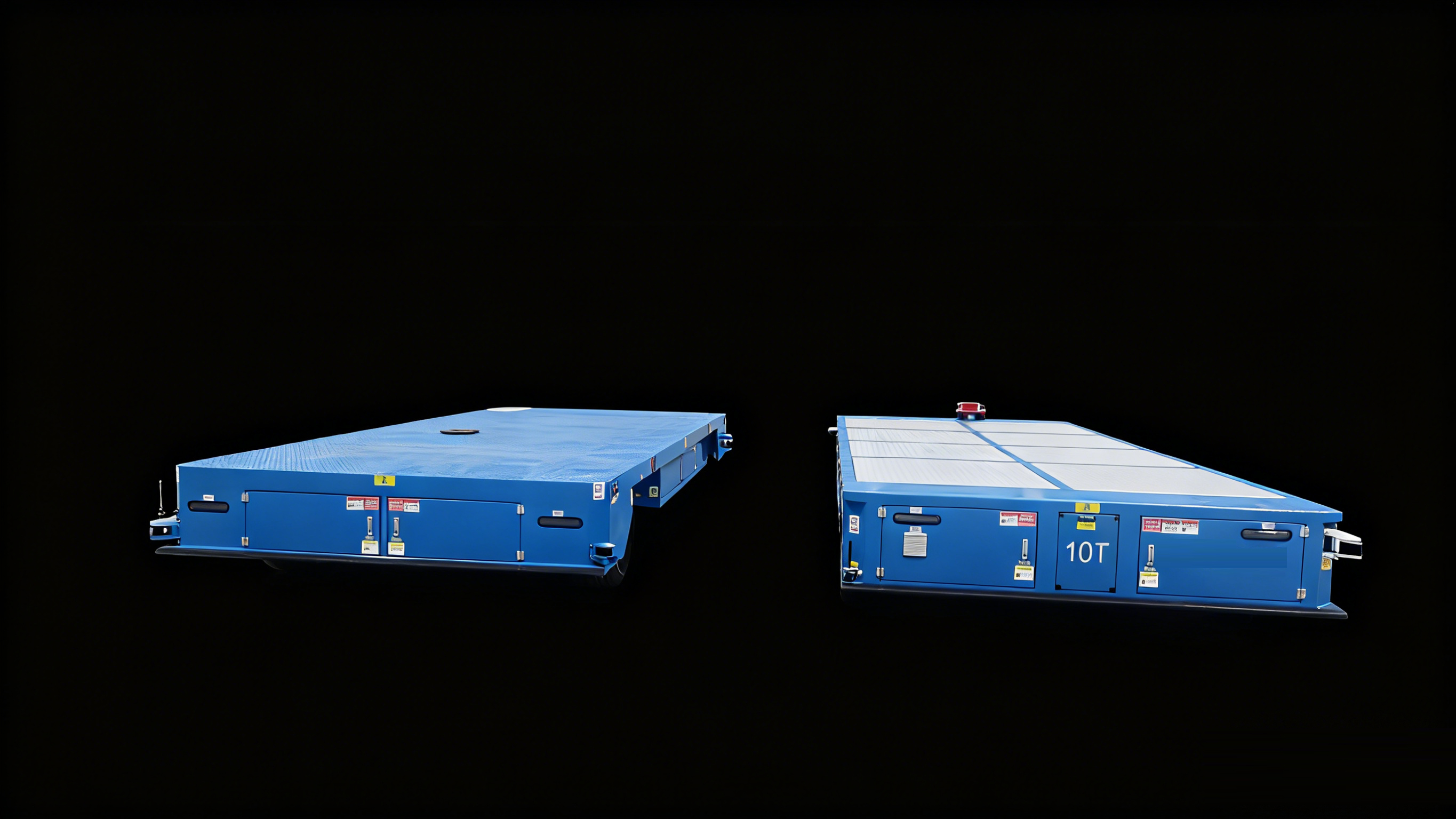
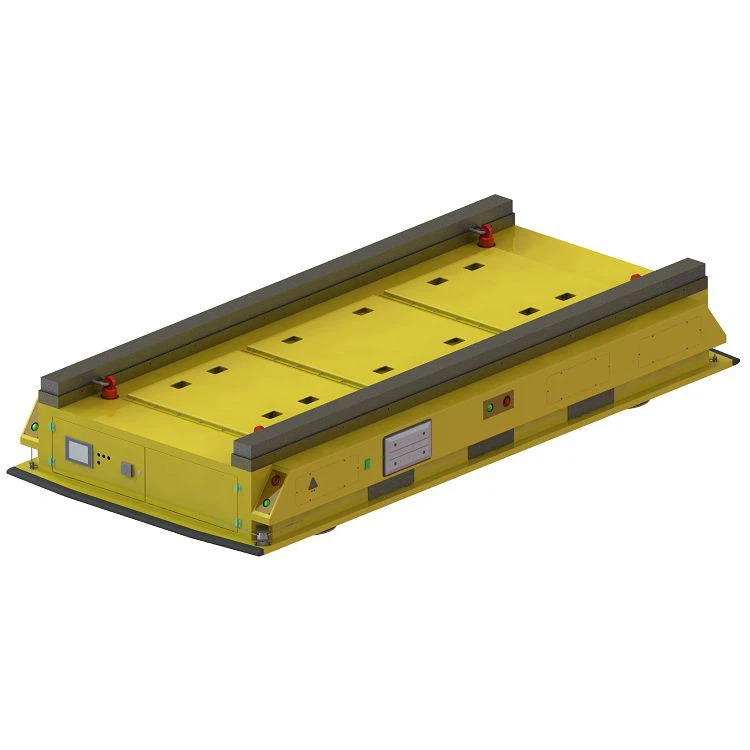
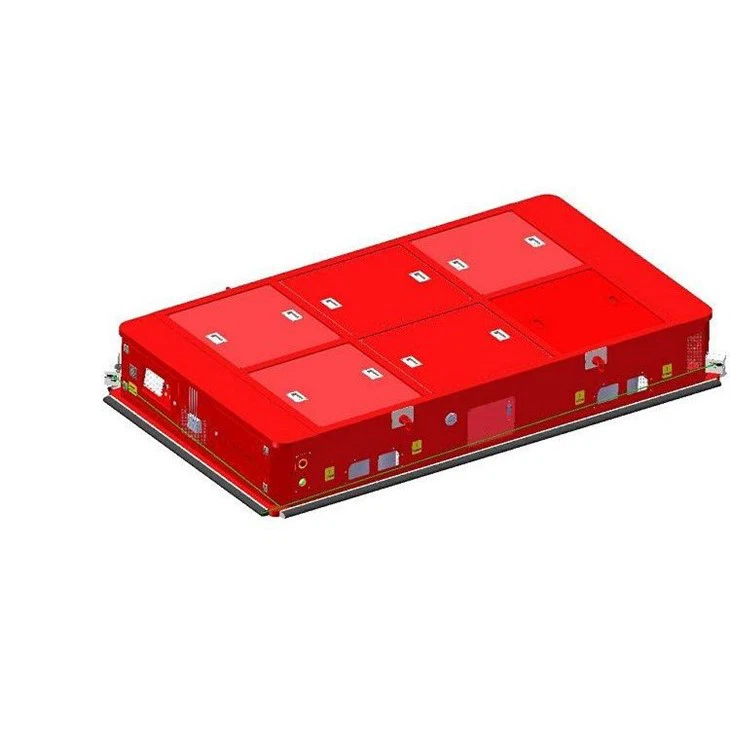
Types of Automated Guided Vehicles
Different AGV models are designed for different industrial tasks:
- AGV Forklifts: Capable of lifting, stacking, and transporting pallets automatically.
- Tugger AGVs: Designed to tow multiple carts for assembly lines and long-distance movement.
- Unit Load AGVs: Equipped with conveyors or lift decks for moving boxes, trays, or components.
- Pallet Truck AGVs: Ideal for transporting pallets across warehouses and docks.
- Custom AGVs: Built for specialized industries such as automotive manufacturing, food production, and pharmaceutical logistics.
Key Benefits of AGVs
AGVs offer a wide range of operational advantages:
- Higher Productivity: Operate 24/7 without fatigue, maximizing throughput.
- Improved Safety: Sensors and detection systems prevent collisions and injuries.
- Reduced Labor Costs: Automates repetitive work, allowing human workers to focus on skilled tasks.
- High Precision: Follows accurate routes with consistent performance.
- Scalable Systems: Businesses can expand their AGV fleets as demand grows.
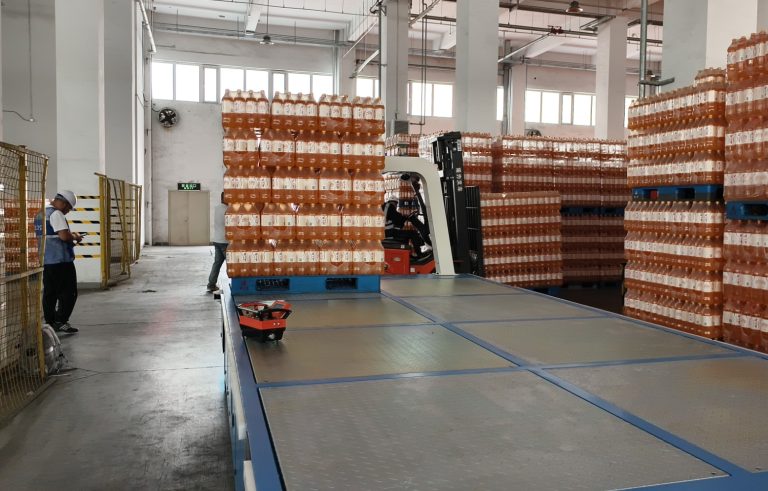
Common Industrial Applications
AGVs support material handling in many sectors:
- Manufacturing: Part delivery, assembly line feeding, WIP transportation.
- Warehousing: Pallet transport, storage, order fulfillment.
- Automotive: Movement of components, engines, and assemblies.
- Food & Beverage: Clean, contamination-free logistics in hygienic environments.
- Pharmaceuticals: High-precision movement in sterile and controlled facilities.
AGVs vs. AMRs: What’s the Difference?
Although both AGVs and Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) automate transport tasks, their navigation differs significantly.
AGVs follow fixed routes, making them ideal for predictable workflows. AMRs, however, use AI-driven navigation and dynamic path planning to adapt to changes in the environment. Companies choose between AGVs and AMRs based on workflow stability, budget, and flexibility requirements.
Why AGVs Matter in Smart Factories
AGVs play a vital role in Industry 4.0 systems. When integrated with ERP, WMS, and MES platforms, AGVs help achieve real-time inventory tracking, automated scheduling, and streamlined production cycles. Their reliability, precision, and compatibility with intelligent management systems make AGVs essential equipment for modern smart factories.
Conclusion
Automated Guided Vehicles are transforming material handling operations by improving efficiency, reducing costs, and enhancing workplace safety. Whether used in warehouses, factories, or distribution centers, AGVs offer a scalable and dependable automation solution. For companies looking to optimize intralogistics and move toward smart manufacturing, AGVs are an indispensable technology for the future.